Scientists from Rice University have improved their graphene substrate deicer to prevent condensate formation of ice when below the freezing point, but also increase the super-hydrophobic nature. This strong film is suitable for relative extreme environments, such as aircraft, ships and power lines.
Scientists from American Rice University have optimized their graphene substrate deicers. Even at ultra-low temperature,the new material can melt the ice of the wing and the wires, and if the temperature is higher than 7 degrees Fahrenheit, ice can't form. James Tour chemistry laboratory,endow such deicer super-hydrophobic properties, and make it can passively prevent moisture condensation at above 7 degrees Fahrenheit. How this film is formed? The de-icing agent is dispersed on the surface of the atom thick graphene nanoribbons.Since the graphene is a conductor, the material can be heated through electric current to melt snow and ice.
According to the researchers, this material can spray to cover, let it be applicable in a wider range, such as aircraft, power lines, radar cover and boats. The study will be published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society this month. "We have learned to make an anti-ice materials, which can be performed under relatively mild conditions, so that heat is no longer a necessary condition, but can be optionally used." Professor Tour said: "Our existing film can be made in a wide range of conditions to prevent a large area from adsorption of snow and ice. "
Hydrophobic material refers to when their contact angle with water is greater than 150 degrees; "contact angle"refers to when the water surface and the material surface contact ,angle between the two planes posed. The larger drops, the greater the contact angle. The contact angle is 0 degrees, then basically a puddle; the maximum angle of 180 degrees, then defined as new to the surface of the water droplets.
Rice University's film combined with fluoride and the graphene nanoribbon to improve their hydrophobic nature. Tour said, they found nanoribbons perfluoro chain with adjustment, will lead the film has a high contact angle, pointing out the film under some special case is controllable.
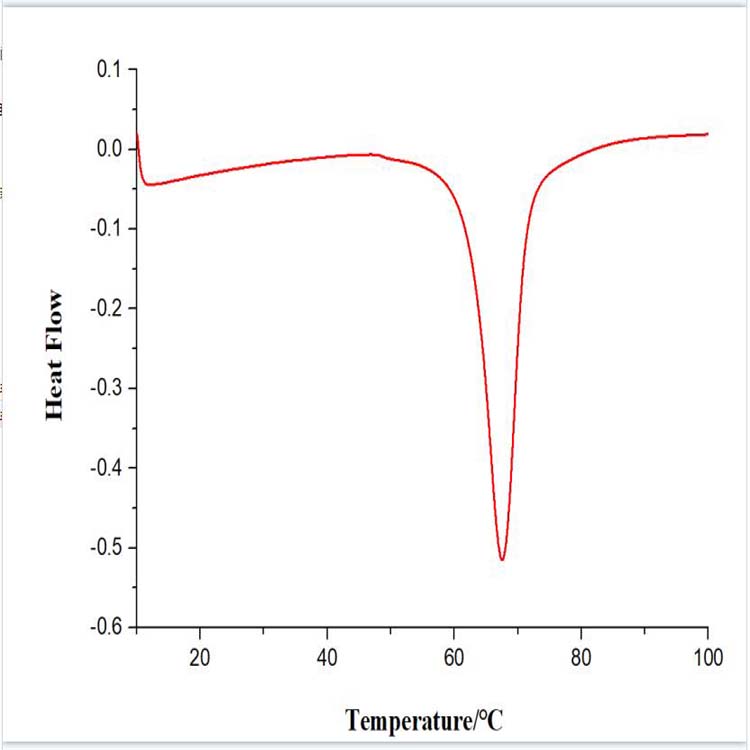
Heating test: the surface is heated to room temperature, then cooled again, discovering the nature of the film and did not change.
The researchers found that when 7 ° C or less, water will condense inside the pore structure, resulting in the loss of super-hydrophobic surface and its anti-ice performance. In this regard, it shall be at least 12 volt electrical heating, then it would be sufficient to maintain the hydrophobic nature. With 40 vodka to heat the film can make it up to room temperature, although the surrounding environment was minus 25 ° C.
The researchers found that it's effective, but the de-icing method still can not completely ruled out water, because some will be left in the belt between the nano-pores. Add some low melting point (-61 ° F) lubricant onto the film to make a smooth surface, and de-icing energy saving acceleration.
by Corrine

 English
English français
français Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский italiano
italiano español
español português
português 日本語
日本語 한국의
한국의 Türkçe
Türkçe














 8620-87226359,8620-87748917
8620-87226359,8620-87748917