Nano tungsten oxide is a powder metallurgy raw material for producing hard alloys and tungsten products. Through powder metallurgy, tungsten carbide hard alloys, superhard molds, tungsten bars, tungsten wires, etc. are manufactured. It can also be used for X-ray screens and fireproof fabrics, as well as colorants and analytical reagents for ceramics.
The color of nano tungsten oxide, in the W-O system, there are tungsten oxides such as WO3, WO 2.9, WO 2.72, and WO2. WO3 (yellow) -- WO 2.90 (blue) - WO 2.72, (purple) - WO2 (brown) - W (gray black). That is, tungsten has four stable oxides: yellow oxide (WO3), blue oxide (WO2.90), purple oxide (WO2.72) and brown oxide (WO2).
Blue tungsten oxide refers to a series of non-stoichiometric oxides of tungsten. The chemical formula is expressed as WOx, mainly WO2.9. Blue tungsten oxide is used to produce tungsten powder, doped tungsten powder, tungsten bars and hard alloys, anti-ultraviolet, photocatalysis, etc. Blue tungsten oxide will change color when exposed to light, and will become a light blue. If it is repacked in a black opaque bag, it will return to its original color.
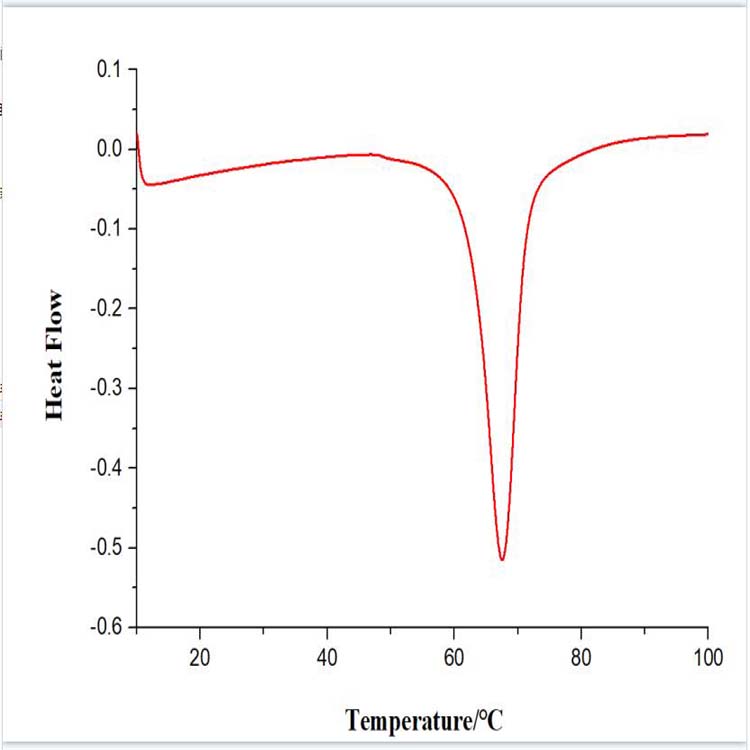
Nano tungsten trioxide (yellow tungsten oxide, WO3) is a lemon yellow powder with a density of 7.2~7.4g/cm3, a melting point of about 1470℃, a boiling point between 1700~2000℃, and significant sublimation above 800℃. The heat of formation of tungsten trioxide is 202.8 cal/mol. Tungsten anhydride is slightly soluble in water (0.2g/L) and insoluble in all inorganic acids except hydrofluoric acid. Tungstic acid is easily soluble in caustic soda solution (NaOH or KOH) and ammonia water to form tungstates [NaWO4, K2WO4 and (NH4)2WO4]. Tungsten trioxide dissolves slowly in ammonia solution, and dissolves more slowly when heated to high temperature. Tungsten trioxide is easily reduced by various reducing agents. At room temperature, even a small amount of organic matter can reduce it and change its color. But when heated in air, it returns to its original color. At 700~900℃, tungsten trioxide can be easily reduced to metallic tungsten by hydrogen, carbon monoxide and carbon.
Nano tungsten dioxide is a brown chocolate-like powder that is sensitive to moisture. When heated, the color changes from light to dark, turning into dark orange, and it returns to its original color after cooling. The density is 10.9~11.1g/cm3, the boiling point is about 1700℃, the heat of generation is 134 kcal/mol, and hydrogen reduces tungsten trioxide to tungsten dioxide at 575~600℃. Tungsten dioxide is insoluble in water, alkaline solution, hydrochloric acid and dilute sulfuric acid. Nitric acid can oxidize tungsten dioxide to high-valent oxides. Tungsten dioxide is quickly oxidized to tungsten trioxide in the air, and turns into blue oxide when heated to 500℃ in nitrogen oxide. At 1020℃, tungsten dioxide can be reduced to metallic tungsten by carbon. When tungsten trioxide is reduced with hydrogen or carbon monoxide at 250~300℃, or when tungsten trioxide is heated to 200~250℃ in vacuum, powdered purple tungsten oxide (WO2.72) can be obtained.

 English
English français
français Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский italiano
italiano español
español português
português 日本語
日本語 한국의
한국의 Türkçe
Türkçe














 8620-87226359,8620-87748917
8620-87226359,8620-87748917